Tendonitis treatment
Schedule an appointment with a professional rheumatologist consultant to get rid of tendon pains caused by Tendonitis disease. Tap the button below to fill the contact form.
What is Tendonitis?
Tendonitis (also spelled tendinitis) is a swelling of a tendon or tendons which connect muscle to bone. The condition can be acute or chronic, depending on its cause. It is common in athletes and others who perform repetitive motions or risk injury to tendons. The condition most typically occurs in the knee, thumb, elbow, shoulder, and heel as a result of injury or repetitive use.
Common forms of tendonitis include golfer’s elbow, tennis elbow, and swimmer’s shoulder, among others. Most forms of the condition can be successfully treated with little intervention. Those with rheumatoid arthritis or blood or kidney diseases are more at risk of developing tendonitis.

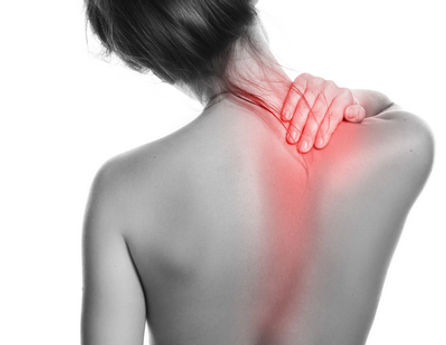
Symptoms of Tendonitis
The most common symptoms of tendonitis are pain and swelling around a joint. Pain may be accompanied by tenderness at the joint. The condition can occur at any age, but the older someone is, the more inflexible their tendons become; thus, they are more prone to injury.
People whose occupations involve repetitive motions, including overhead reaching, use of force, vibrations, and awkward positions are more at risk of developing tendinitis, as are athletes. Most forms of tendonitis can be treated with rest and over the counter medication in order to alleviate or completely relieve symptoms. Failure to seek treatment can result in tendonitis, a more serious condition, and even ruptured tendons.
Tendonitis may resolve itself, especially if the affected area is rested or immobilized. The most common recommendation is “RICE” – rest, ice, compression, elevation. Analgesics including acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, and corticosteroids are often prescribed as are physical or occupational therapies.
Prevention involves awareness of repetitive motions at work, or in sport, and a conscious effort to reduce force. Paying attention to posture, form, and technique may help. Taking breaks and stretching can also help, as can maintaining a warm work environment. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet, exercise, and rest is also important.
Treatment of tendon pains







